About Thailand
Thailand is an important country in Southeast Asia and major factor in the operation of “One Belt One Road”

One Belt One Road
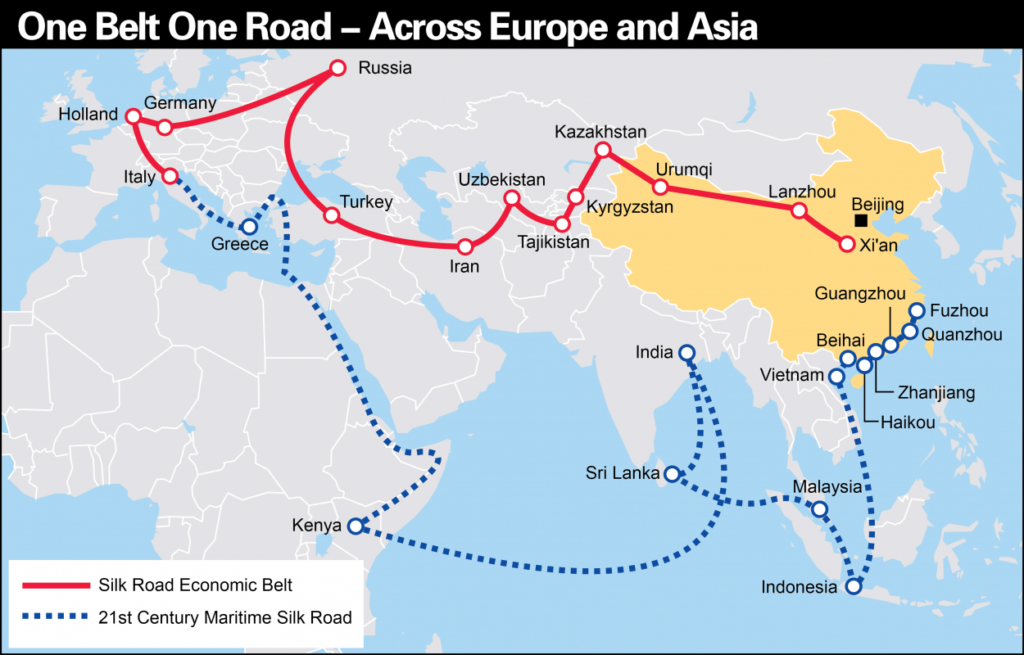
In September 2013, Xi Jin Ping President of China has visited Kazakstan and firstly proposed an idea to cooperate in “Silk Road Economic Belt” that will connect China, Central Asia and Europe through land, train and air transportation with modern technology. During his visit to Indonesia in October 2013, he has proposed strategic plan of “21st Century Maritime Silk Road” which will connect Chinese Seaport in Southeast Asia, South Asia, Middle East and Europe through land and sea transportation, this will enhance seaport construction investment and establish an industrial and trade center.
New Silk Road divided into “Silk Road Economic Belt” and “21st Century Maritime Silk Road” development goals are economic connection of Asia, Europe and Africa. This Silk Road will bring changes to economy, politics and society. It is the most valuable development strategy in the international standard. New Silk Road cover 65 countries in 6 regions, such as Southeast Asia, Central Asia, Middle East, North Africa, South Asia and Europe. Populations of the countries along Silk Road is 62.3% of worldwide populations. Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is 30% of worldwide GDP. Household consumption is 24% of worldwide consumption. “One Belt One Road” will become the largest infrastructure construction project in the world.
New Silk Road consists of project and development plan in strategic areas. First to develop the commercial center city in all regions, then expand and connect with the same network as we often hear about “Belt and Road”
One Belt
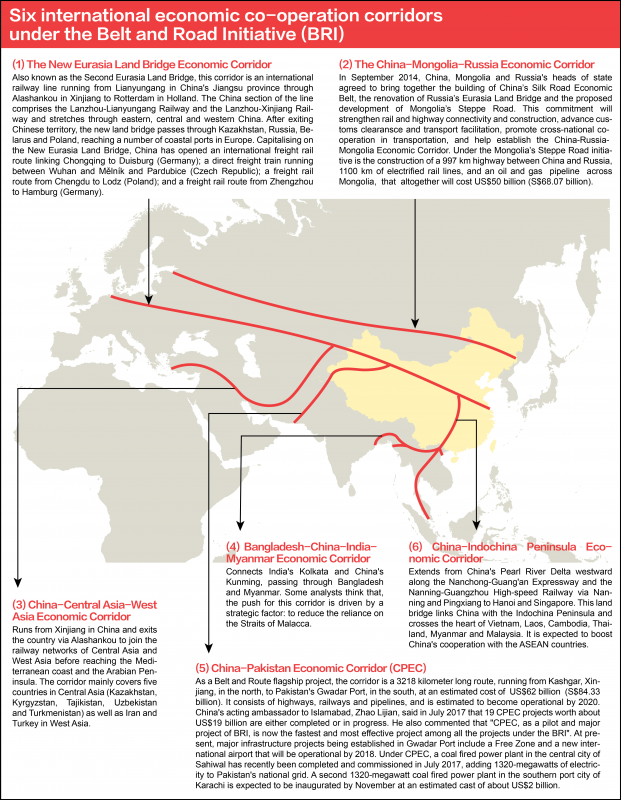
One Belt means the “Silk Road” economic belts, a land network connecting China with six regions: Southeast Asia, Central Asia, South Asia, Middle East, North Africa and Europe, divided into 6 development routes or economic corridors. The coastal economic corridor is also connected to the sea corridor. Each of these economic corridors focuses on building infrastructure to improve transportation efficiency such as road, railway, port and oil pipelines. In addition, there are also construction and development of facilities to facilitate the transportation center and to support trade growth such as special economic zone, border port, customs port, etc. Six economy corridors are as follows:
- New Eurasia Land Bridge (NELB)
- China-Mongolia-Russia Economic Corridor (CMREC)
- China-Central Asia-West Asia Economic Corridor
- China Peninsula-Indochina Peninsula Economic Corridor
- China-Pakistan Economic Corridor
- China-India-Myanmar Economic Corridor
One Belt One Road
One Belt One Road is “21st Century Maritime Silk Road”which is a shipping channel connecting China and other ocean countries. China has developed 4 major ports to support the new Silk Road, for example, Fuzhou Port, Quanzhou Port, Guangzhou Port, and Zhanjiang Port (as picture 3). The route is divided into 2 routes:
- East Coast of China-South China Sea-Indian Ocean-Persian Gulf-Mediterranean Sea-Europe
- East Coast of China-South China Sea-South Pacific
Read more: beltandroad.zaobao.com/beltandroaden/concept
What is“RCEP”
RCEP (Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership) is regional economic partnership agreement. It is a large scale trade treaty proposed by ASEAN to promote trade among member countries and trade with partners in the world’s largest Free Trade Agreement (FTA), effective 1st January 2022. RCEP has 15 members: 10 Asean countries, Japan, South Korea, China, Australia and New Zealand, total population in RCEP is 2,300 million people (30.2% of world population). Total GDP of 28.5 trillion (33.6% of world GDP) and total trade value is 10.7 trillion US dollars (30.3% of world trade value).
RCEP will help facilitate trade members, abolish import duties collected on 39,366 Thai products. Perishable items will be inspected for customs clearance within 6 hours and normal goods within 48 hours. Opportunities to expand service businesses from Thailand to RCEP member countries such as construction, retail, health, movie and entertainment, etc.
In term of investment, RCEP is an important tool to help Thailand stay in the global chain in Asia. This makes investment in the region more attractive. There are policies to facilitate investment in expanding production bases of foreign companies in Thailand and help promote the establishment of distribution bases of Thai products abroad and foreign products.
RCEP is a modern, comprehensive, high quality, mutually beneficial, free trade area for products, service and investment. In addition, there has been an increase in cooperation in various fields such as electronic commerce, intellectual property, commercial competition, new business such as Small Medium Enterprise (SME).
Bright future in 2022
Thailand
Inflation ( % )
2.7
Total GDP (Billion USD)
243
GDP Expansion Rate ( % )
3.57
GDP per Capita (Billion bathThai)
18,275
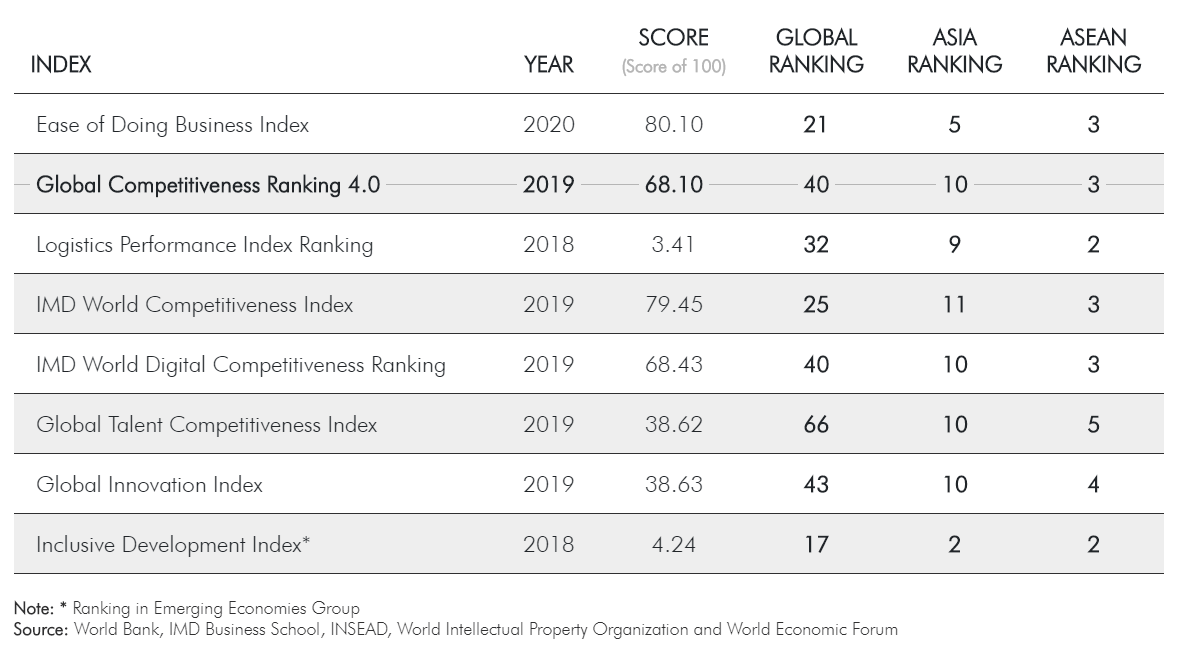
Position of Thailand in Global, Asia and ASEAN Rankings
Readmore : eng.eeco.or.th/en/government-initiative
ASEAN
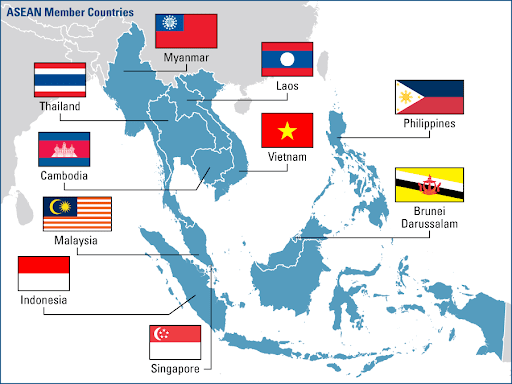
Association of South East Asian Nations (ASEAN) established on 8th August 1967 at Bangkok. ASEAN has 5 member countries consists of Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore and Thailand, signed and declare Bangkok Declaration or ASEAN Declaration.
Brunei joined ASEAN on 7th January 1984. Vietnam joined ASEAN on 28th July 1995. Lao and Myanmar joined ASEAN on 23rd July 1997. Cambodia joined ASEAN 30th April 1999. Until 2020, there are 10 members of ASEAN.
Goals and Objectives
The objectives of the declaration of ASEAN are as follows:
- To promote cooperation and mutual assistance in the economy, society, culture, technology, science and administration.
- To promote regional peace and security
- To foster economic prosperity and cultural development in the region
- To promote people in ASEAN to have a good life and quality of life.
- To provide mutual assistance in the form of training and research, and to promote Southeast Asian education.
- To increase the efficiency of agriculture and industry expanding trade as well as improving transport and communication.
- To strengthen ASEAN cooperation with external countries cooperation organization of other regions and international organizations.

Basic Principles
Managing State-to-State relations each, each ASEAN member state must comply with “Treaty of Amity and cooperation in Southeast Asia” adopted in 2019. Basic principles set out in the treaty are as follows:
- Mutual respect for independence, sovereignty, equality. Integration of territories and national identity of all nations
- The rights of every state to exist without interference, the overthrow of sovereignty or external coercion.
- The principle of not interfering in each other’s internal affairs.
- Settle differences or disputes by peaceful means
- Not using coercion or use of force
- Effective cooperation between member states
ASEAN Community
On the 30th anniversary of the founding of ASEAN, “ASEAN Vision 2020”, has been recorded jointly by the ASEAN member countries with a focus on peace, stability, prosperity, development and promotion of sustainable development of society and community.
At the 9th ASEAN Summit in 2003, the leaders of countries vote for the establishment of ASEAN Community.
At the 12th ASEAN Summit in January 2007, leaders of different countries has reaffirmed its unwavering commitment to accelerate the establishment of the ASEAN Community in 2015 and signing the Cebu Declaration on the Accelerating the Establishment of the ASEAN Community in 2015.
ASEAN Community consists of three main communities: the “ASEAN Political Security Community”, the “ASEAN Economic Community” and “ASEAN Social and Cultural Community” which is under “ASEAN Integration Initiative II” and “ASEAN Community Work Plan 2009-2015”. Each congregation has its own pattern and common pattern.
ASEAN Charter
“ASEAN Charter” establishes ASEAN as a legal status and institutional framework. Laying a solid foundation for the establishment of the ASEAN Community. In addition, standards, rules, and values of ASEAN have also been established. Set clear goals for ASEAN development and address the responsibilities of Contracting States and the implementation of the ASEAN Charter.
ASEAN Charter effective on 15th December 2008, the same time with the ASEAN’s Foreign Ministers’ Meeting was held at the ASEAN Secretariat in Jakarta in commemorate important events in ASEAN.
After “ASEAN Charter” comes into force ASEAN will work under a new legal framework and establish several new institutions to promote the ASEAN Community building process.
ASEAN Charter has become a legally binding agreement between the 10 ASEAN Member States.
Readmore : asean.org
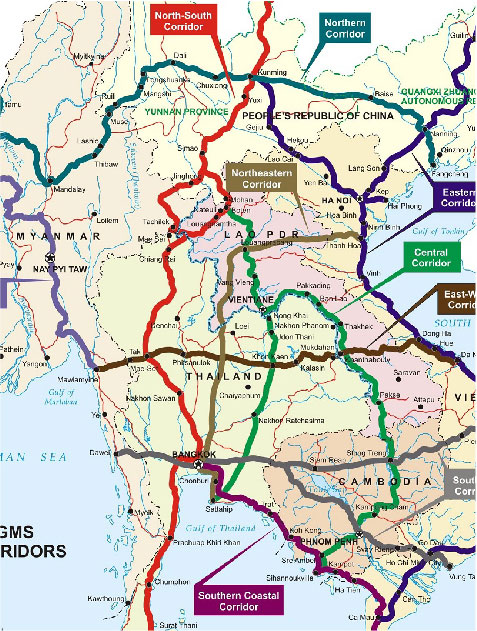
Economic Cooperation Development Project in Greater Mekong Subregion
Economic Cooperation Development Project in Greater Mekong Subregion or economic hexagon is a cooperation of 6 countries, Thailand, Myanmar, Laos, Cambodia, China (Yunnan) and Vietnam.
In 1992, under the initiative of the Asian Development Bank of 6 countries, jointly initiated a mechanism for economic cooperation in the Mekong Subregion Economic Cooperation Development Project.

With support from Asia Development Bank and other donors, Economic Cooperation Development Program in the Greater Mekong Subregion (GMS) help carry out important development projects in the region, including agriculture, energy, environment, health, human resource development, information technology, communication, tourism, transportation and freight to facilitate cooperation and development of the city.
To achieve the vision, prosperous, integrated and harmonious subregion development, GMS has implemented the followings a three pronged development strategy (3C strategy).
- Strengthen regional connectivity by building sustainable physical infrastructure and transforming transport routes into a multinational economy.
- Improve regional competitiveness by promoting efficient flow of people and goods across borders.
- Through the development of projects to solve social and environmental problems together and create a wider awareness in the community.
Since 1992, Economic Cooperation Development Project in GMS has made great progress and more than 20 billion US dollars have been directly invested through the project. The rich natural resources of GMS have become a source of income for most of the region’s population, particularly agriculture Mekong countries are gradually shift from sufficiency agriculture to a more diversified economy. The model that corresponds to this trend is strengthening trade relations between 6 countries, especially trade, investment and cross-border trade, migrant workers, natural resources, including water for agriculture, fishery, oil and minerals remains important to the growth of GMS, rich in plants and animals from the North Malay Peninsula to Thailand, extending to the foothills of Himalayas from wide river valleys to tropical rainforests. After 10 million years of natural evolution and sea level change, the Cardamom Mountains and Annamite Mountains, the Indochina’s region Mountains has left behind a unique lifestyle and rich heritage. The mountains cross through countries such as Lao, Cambodia, Thailand and Vietnam. The abundant human and natural resources of Mekong region have made Xinjiang Autonomous Region grow Asia’s economy. The Mekong Subregion has the potential to become one of the fastest growing regions in the world.
Economic route of the Mekong Subregion Economic Cooperation Development Project
Economic route of the Mekong Subregion Economic Cooperation Development Project is cooperation area along important routes along with a variety of social and economic activities, including economic and social development areas such as factories, tourism, trade and environmental conservation activities.
The construction of economic routes of economic cooperation development projects in the GMS are more complex than the highways linking the two cities. It is not only related to the construction and development of infrastructure but also includes laws and regulations that allow entrepreneurs to enter the market, as well as other activities that fully support trade and development.
The economic route benefits of the GMS Economic Cooperation Development Project has more benefits than other projects. There are three important economic routes in GMS and it is planned to expand the development of these economic corridors and strengthen the capital cities in GMS.
Readmore : greatermekong.org
Thailand4.0
Thailand 4.0 is economic model that aims to support the country from the many economic challenges arising from the traditional economic development model focused on agricultural development (Thailand 1.0), Light Industry Era (Thailand 2.0) and Value Added Industry Era (Thailand 3.0) especially the “middle income trap”, the “inequality trap”, and the “development imbalance trap” found in Thailand 3.0
Goals of Thailand4.0 Economic Model

- Economic Prosperity: To create a high value added, innovation-driven economy. This model aims to increase R&D cost to 4% of GDP and increase 6% economic growth rate in 5 years. By the year 2032, income per capita will be US$5,470
- Social well-being: Building a progressive society together. Value the potential of all members of society not allowing other people and society to destroy the development in those days. The goal is to reduce social inequality from 0.465 to 0.36 within 20 years from 2013 to 2032, and integrate into the social welfare system and develop at least 20,000 households into “Smart Farmer” within 5 years.
- “Human Value in the 21stCentury” and “Thailand 4.0” will increase Thailand’s HDI from 0.722 to 0.8 within 10 years or in the top 50 of the country in 20 years, at least 5 Thai Universities are ranked among the top 100 higher education institutions in the world.
- Environmental Conservation: create a livable society, build an economy that adapts to climate change, build low carbon society. The goal is to develop at least 10 most livable cities in the world in order to reduce the risk of terrorism.